blessed
A curses-like library for node.js.
Install
$ npm install blessed
Example
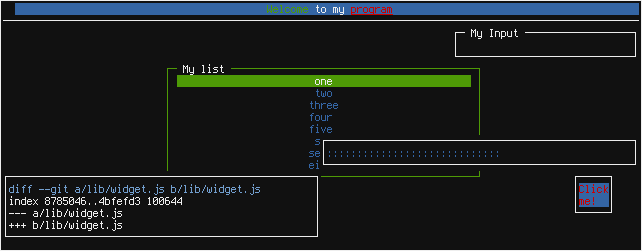
This will render a box with line borders containing the text 'Hello world!',
perfectly centered horizontally and vertically.
var blessed = require('blessed');
// Create a screen object.
var screen = blessed.screen();
screen.title = 'my window title';
// Create a box perfectly centered horizontally and vertically.
var box = blessed.box({
top: 'center',
left: 'center',
width: '50%',
height: '50%',
content: 'Hello {bold}world{/bold}!',
tags: true,
border: {
type: 'line'
},
style: {
fg: 'white',
bg: 'magenta',
border: {
fg: '#f0f0f0'
},
hover: {
bg: 'green'
}
}
});
// Append our box to the screen.
screen.append(box);
// Add a PNG icon to the box (X11 only)
var icon = blessed.image({
parent: box,
top: 0,
left: 0,
width: 'shrink',
height: 'shrink',
file: __dirname + '/my-program-icon.png'
});
// If our box is clicked, change the content.
box.on('click', function(data) {
box.setContent('{center}Some different {red-fg}content{/red-fg}.{/center}');
screen.render();
});
// If box is focused, handle `enter`/`return` and give us some more content.
box.key('enter', function(ch, key) {
box.setContent('{right}Even different {black-fg}content{/black-fg}.{/right}\n');
box.setLine(1, 'bar');
box.insertLine(1, 'foo');
screen.render();
});
// Quit on Escape, q, or Control-C.
screen.key(['escape', 'q', 'C-c'], function(ch, key) {
return process.exit(0);
});
// Focus our element.
box.focus();
// Render the screen.
screen.render();
Windows compatibility
Currently there is no mouse or resize event support on Windows.
Windows users will need to explicitly set term when creating a screen like so
(NOTE: This is no longer necessary as of the latest versions of blessed.
This is now handled automatically):
var screen = blessed.screen({ term: 'windows-ansi' });
High-level Documentation
Widgets
Blessed comes with a number of high-level widgets so you can avoid all the nasty low-level terminal stuff.
Node (from EventEmitter)
The base node which everything inherits from.
Options:
- screen - the screen to be associated with.
- parent - the desired parent.
- children - an arrray of children.
Properties:
- inherits all from EventEmitter.
- type - type of the node (e.g.
box). - options - original options object.
- parent - parent node.
- screen - parent screen.
- children - array of node's children.
- data, _, $ - an object for any miscellanous user data.
- index - render index (document order index) of the last render call.
Events:
- inherits all from EventEmitter.
- adopt - received when node is added to a parent.
- remove - received when node is removed from it's current parent.
- reparent - received when node gains a new parent.
- attach - received when node is attached to the screen directly or somewhere in its ancestry.
- detach - received when node is detached from the screen directly or somewhere in its ancestry.
Methods:
- inherits all from EventEmitter.
- prepend(node) - prepend a node to this node's children.
- append(node) - append a node to this node's children.
- remove(node) - remove child node from node.
- insert(node, i) - insert a node to this node's children at index
i. - insertBefore(node, refNode) - insert a node to this node's children before the reference node.
- insertAfter(node, refNode) - insert a node from node after the reference node.
- detach() - remove node from its parent.
- emitDescendants(type, args..., [iterator]) - emit event for element, and recursively emit same event for all descendants.
- get(name, [default]) - get user property with a potential default value.
- set(name, value) - set user property to value.
Screen (from Node)
The screen on which every other node renders.
Options:
- program - the blessed Program to be associated with.
- smartCSR - attempt to perform CSR optimization on all possible elements (not just full-width ones, elements with uniform cells to their sides). this is known to cause flickering with elements that are not full-width, however, it is more optimal for terminal rendering.
- fastCSR - do CSR on any element within 20 cols of the screen edge on
either side. faster than
smartCSR, but may cause flickering depending on what is on each side of the element. - useBCE - attempt to perform
back_color_eraseoptimizations for terminals that support it. it will also work with terminals that don't support it, but only on lines with the default background color. as it stands with the current implementation, it's uncertain how much terminal performance this adds at the cost of overhead within node. - resizeTimeout - amount of time (in ms) to redraw the screen after the terminal is resized (default: 300).
- tabSize - the width of tabs within an element's content.
- autoPadding - automatically position child elements with border and padding in mind.
- log - create a log file. see
logmethod. - dump - dump all output and input to desired file. can be used together
with
logoption if set as a boolean. - debug - debug mode. enables usage of the
debugmethod. - ignoreLocked - Array of keys in their full format (e.g.
C-c) to ignore when keys are locked. Useful for creating a key that will always exit no matter whether the keys are locked.
Properties:
- inherits all from Node.
- program - the blessed Program object.
- tput - the blessed Tput object (only available if you passed
tput: trueto the Program constructor.) - focused - top of the focus history stack.
- width - width of the screen (same as
program.cols). - height - height of the screen (same as
program.rows). - cols - same as
screen.width. - rows - same as
screen.height. - left, rleft - left offset, always zero.
- right, rright - right offset, always zero.
- top, rtop - top offset, always zero.
- bottom, rbottom - bottom offset, always zero.
- grabKeys - whether the focused element grabs all keypresses.
- lockKeys - prevent keypresses from being received by any element.
- hover - the currently hovered element. only set if mouse events are bound.
- title - set or get window title.
Events:
- inherits all from Node.
- resize - received on screen resize.
- mouse - received on mouse events.
- keypress - received on key events.
- element [name] - global events received for all elements.
- key [name] - received on key event for [name].
- focus, blur - received when the terminal window focuses/blurs. requires a terminal supporting the focus protocol and focus needs to be passed to program.enableMouse().
- prerender - received before render.
- render - received on render.
Methods:
- inherits all from Node.
- log(msg, ...) - write string to the log file if one was created.
- debug(msg, ...) - same as the log method, but only gets called if the
debugoption was set. - alloc() - allocate a new pending screen buffer and a new output screen buffer.
- draw(start, end) - draw the screen based on the contents of the screen buffer.
- render() - render all child elements, writing all data to the screen buffer and drawing the screen.
- clearRegion(x1, x2, y1, y2) - clear any region on the screen.
- fillRegion(attr, ch, x1, x2, y1, y2) - fill any region with a character of a certain attribute.
- focusOffset(offset) - focus element by offset of focusable elements.
- focusPrevious() - focus previous element in the index.
- focusNext() - focus next element in the index.
- focusPush(element) - push element on the focus stack (equivalent to
screen.focused = el). - focusPop() - pop element off the focus stack.
- saveFocus() - save the focused element.
- restoreFocus() - restore the saved focused element.
- rewindFocus() - "rewind" focus to the last visible and attached element.
- key(name, listener) - bind a keypress listener for a specific key.
- onceKey(name, listener) - bind a keypress listener for a specific key once.
- unkey(name, listener) - remove a keypress listener for a specific key.
- spawn(file, args, options) - spawn a process in the foreground, return to blessed app after exit.
- exec(file, args, options, callback) - spawn a process in the foreground, return to blessed app after exit. executes callback on error or exit.
- readEditor([options], callback) - read data from text editor.
- setEffects(el, fel, over, out, effects, temp) - set effects based on two events and attributes.
- insertLine(n, y, top, bottom) - insert a line into the screen (using csr: this bypasses the output buffer).
- deleteLine(n, y, top, bottom) - delete a line from the screen (using csr: this bypasses the output buffer).
- insertBottom(top, bottom) - insert a line at the bottom of the screen.
- insertTop(top, bottom) - insert a line at the top of the screen.
- deleteBottom(top, bottom) - delete a line at the bottom of the screen.
- deleteTop(top, bottom) - delete a line at the top of the screen.
Element (from Node)
The base element.
Options:
- fg, bg, bold, underline - attributes.
- style - may contain attributes in the format of:
{
fg: 'blue',
bg: 'black',
border: {
fg: 'blue'
},
scrollbar: {
bg: 'blue'
},
focus: {
bg: 'red'
},
hover: {
bg: 'red'
}
}
- border - border object, see below.
- content - element's text content.
- clickable - element is clickable.
- input - element is focusable and can receive key input.
- focused - element is focused.
- hidden - whether the element is hidden.
- label - a simple text label for the element.
- hoverText - a floating text label for the element which appears on mouseover.
- align - text alignment:
left,center, orright. - valign - vertical text alignment:
top,middle, orbottom. - shrink - shrink/flex/grow to content and child elements. width/height during render.
- padding - amount of padding on the inside of the element. can be a number
or an object containing the properties:
left,right,top, andbottom. - width, height - width/height of the element, can be a number, percentage
(
0-100%), or keyword (halforshrink). - left, right, top, bottom - offsets of the element relative to its
parent. can be a number, percentage (
0-100%), or keyword (center).rightandbottomdo not accept keywords. - position - can contain the above options.
- scrollable - whether the element is scrollable or not.
- ch - background character (default is whitespace
Properties:
- inherits all from Node.
- name - name of the element. useful for form submission.
- border - border object.
- type - type of border (
lineorbg).bgby default. - ch - character to use if
bgtype, default is space. - bg, fg - border foreground and background, must be numbers (-1 for default).
- bold, underline - border attributes.
- type - type of border (
- style - contains attributes (e.g.
fg/bg/underline). see above. - position - raw width, height, and offsets.
- content - raw text content.
- hidden - whether the element is hidden or not.
- visible - whether the element is visible or not.
- detached - whether the element is attached to a screen in its ancestry somewhere.
- fg, bg - foreground and background, must be numbers (-1 for default).
- bold, underline - attributes.
- width - calculated width.
- height - calculated height.
- left - calculated absolute left offset.
- right - calculated absolute right offset.
- top - calculated absolute top offset.
- bottom - calculated absolute bottom offset.
- rleft - calculated relative left offset.
- rright - calculated relative right offset.
- rtop - calculated relative top offset.
- rbottom - calculated relative bottom offset.
Events:
- inherits all from Node.
- blur, focus - received when an element is focused or unfocused.
- mouse - received on mouse events for this element.
- mousedown, mouseup - mouse button was pressed or released.
- wheeldown, wheelup - wheel was scrolled down or up.
- mouseover, mouseout - element was hovered or unhovered.
- mousemove - mouse was moved somewhere on this element.
- keypress - received on key events for this element.
- move - received when the element is moved.
- resize - received when the element is resized.
- key [name] - received on key event for [name].
- prerender - received before a call to render.
- render - received after a call to render.
Methods:
- inherits all from Node.
- note: if the
scrollableoption is enabled, Element inherits all methods from ScrollableBox. - render() - write content and children to the screen buffer.
- hide() - hide element.
- show() - show element.
- toggle() - toggle hidden/shown.
- focus() - focus element.
- key(name, listener) - bind a keypress listener for a specific key.
- onceKey(name, listener) - bind a keypress listener for a specific key once.
- unkey(name, listener) - remove a keypress listener for a specific key.
- onScreenEvent(type, listener) - same as
el.on('screen', ...)except this will automatically cleanup listeners after the element is detached. - setIndex(z) - set the z-index of the element (changes rendering order).
- setFront() - put the element in front of its siblings.
- setBack() - put the element in back of its siblings.
- setLabel(text/options) - set the label text for the top-left corner.
example options:
{text:'foo',side:'left'} - removeLabel() - remove the label completely.
- setHover(text/options) - set the hover text for the bottom-right corner.
example options:
{text:'foo'} - removeHover() - remove the hover label completely.
Content Methods
Methods for dealing with text content, line by line. Useful for writing a text editor, irc client, etc.
Note: all of these methods deal with pre-aligned, pre-wrapped text. If you use deleteTop() on a box with a wrapped line at the top, it may remove 3-4 "real" lines (rows) depending on how long the original line was.
The lines parameter can be a string or an array of strings. The line
parameter must be a string.
- setContent(text) - set the content. note: when text is input, it will be stripped of all non-SGR escape codes, tabs will be replaced with 8 spaces, and tags will be replaced with SGR codes (if enabled).
- getContent() - return content, slightly different from
el.content. assume the above formatting. - setText(text) - similar to
setContent, but ignore tags and remove escape codes. - getText() - similar to
getContent, but return content with tags and escape codes removed. - insertLine(i, lines) - insert a line into the box's content.
- deleteLine(i) - delete a line from the box's content.
- getLine(i) - get a line from the box's content.
- getBaseLine(i) - get a line from the box's content from the visible top.
- setLine(i, line) - set a line in the box's content.
- setBaseLine(i, line) - set a line in the box's content from the visible top.
- clearLine(i) - clear a line from the box's content.
- clearBaseLine(i) - clear a line from the box's content from the visible top.
- insertTop(lines) - insert a line at the top of the box.
- insertBottom(lines) - insert a line at the bottom of the box.
- deleteTop() - delete a line at the top of the box.
- deleteBottom() - delete a line at the bottom of the box.
- unshiftLine(lines) - unshift a line onto the top of the content.
- shiftLine(i) - shift a line off the top of the content.
- pushLine(lines) - push a line onto the bottom of the content.
- popLine(i) - pop a line off the bottom of the content.
- getLines() - an array containing the content lines.
- getScreenLines() - an array containing the lines as they are displayed on the screen.
Box (from Element)
A box element which draws a simple box containing content or other elements.
Options:
- inherits all from Element.
Properties:
- inherits all from Element.
Events:
- inherits all from Element.
Methods:
- inherits all from Element.
Text (from Element)
An element similar to Box, but geared towards rendering simple text elements.
Options:
- inherits all from Element.
- fill - fill the entire line with chosen bg until parent bg ends, even if there is not enough text to fill the entire width. (deprecated)
- align - text alignment:
left,center, orright.
Inherits all options, properties, events, and methods from Element.
Line (from Box)
A simple line which can be line or bg styled.
Options:
- inherits all from Box.
- orientation - can be
verticalorhorizontal. - type, bg, fg, ch - treated the same as a border object.
(attributes can be contained in
style).
Inherits all options, properties, events, and methods from Box.
ScrollableBox (from Box)
DEPRECATED - Use Box with the scrollable option instead.
A box with scrollable content.
Options:
- inherits all from Box.
- baseLimit - a limit to the childBase. default is
Infinity. - alwaysScroll - a option which causes the ignoring of
childOffset. this in turn causes the childBase to change every time the element is scrolled. - scrollbar - object enabling a scrollbar. allows
ch,fg, andbgproperties.
Properties:
- inherits all from Box.
- childBase - the offset of the top of the scroll content.
- childOffset - the offset of the chosen item (if there is one).
Events:
- inherits all from Box.
- scroll - received when the element is scrolled.
Methods:
- scroll(offset) - scroll the content by a relative offset.
- scrollTo(index) - scroll the content to an absolute index.
- setScroll(index) - same as
scrollTo. - setScrollPerc(perc) - set the current scroll index in percentage (0-100).
- getScroll() - get the current scroll index in lines.
- getScrollHeight() - get the actual height of the scrolling area.
- getScrollPerc() - get the current scroll index in percentage.
- resetScroll() - reset the scroll index to its initial state.
ScrollableText (from ScrollableBox)
DEPRECATED - Use Box with the scrollable and alwaysScroll options
instead.
A scrollable text box which can display and scroll text, as well as handle pre-existing newlines and escape codes.
Options:
- inherits all from ScrollableBox.
- mouse - whether to enable automatic mouse support for this element.
- keys - use predefined keys for navigating the text.
- vi - use vi keys with the
keysoption.
Properties:
- inherits all from ScrollableBox.
Events:
- inherits all from ScrollableBox.
Methods:
- inherits all from ScrollableBox.
List (from Box)
A scrollable list which can display selectable items.
Options:
- inherits all from Box.
- selectedFg, selectedBg - foreground and background for selected item,
treated like fg and bg. (can be contained in style: e.g.
style.selected.fg). - selectedBold, selectedUnderline - character attributes for selected item,
treated like bold and underline. (can be contained in style: e.g.
style.selected.bold). - itemFg, itemBg - foreground and background for unselected item,
treated like fg and bg. (can be contained in style: e.g.
style.item.fg). - itemBold, itemUnderline - character attributes for an unselected item,
treated like bold and underline. (can be contained in style: e.g.
style.item.bold). - mouse - whether to automatically enable mouse support for this list (allows clicking items).
- keys - use predefined keys for navigating the list.
- vi - use vi keys with the
keysoption. - items - an array of strings which become the list's items.
- search - a function that is called when
vimode is enabled and the key/is pressed. This function accepts a callback function which should be called with the search string. The search string is then used to jump to an item that is found initems.
Properties:
- inherits all from Box.
Events:
- inherits all from Box.
- select - received when an item is selected.
- cancel - list was canceled (when
escis pressed with thekeysoption). - action - either a select or a cancel event was received.
Methods:
- inherits all from Box.
- add/addItem(text) - add an item based on a string.
- getItemIndex(child) - returns the item index from the list. child can be an element, index, or string.
- getItem(child) - returns the item element. child can be an element, index, or string.
- removeItem(child) - removes an item from the list. child can be an element, index, or string.
- clearItems() - clears all items from the list.
- setItems(items) - sets the list items to multiple strings.
- select(index) - select an index of an item.
- move(offset) - select item based on current offset.
- up(amount) - select item above selected.
- down(amount) - select item below selected.
- pick(callback) - show/focus list and pick an item. the callback is executed with the result.
Form (from Box)
A form which can contain form elements.
Options:
- inherits all from Box.
- keys - allow default keys (tab, vi keys, enter).
- vi - allow vi keys.
Properties:
- inherits all from Box.
- submission - last submitted data.
Events:
- inherits all from Box.
- submit - form is submitted. receives a data object.
- cancel - form is discarded.
- reset - form is cleared.
Methods:
- inherits all from Box.
- focusNext() - focus next form element.
- focusPrevious() - focus previous form element.
- submit() - submit the form.
- cancel() - discard the form.
- reset() - clear the form.
Input (from Box)
A form input.
Textarea (from Input)
A box which allows multiline text input.
Options:
- inherits all from Input.
- keys - use pre-defined keys (
iorenterfor insert,efor editor,C-efor editor while inserting). - mouse - use pre-defined mouse events (right-click for editor).
- inputOnFocus - call
readInput()when the element is focused. automatically unfocus.
Properties:
- inherits all from Input.
- value - the input text. read-only.
Events:
- inherits all from Input.
- submit - value is submitted (enter).
- cancel - value is discared (escape).
- action - either submit or cancel.
Methods:
- inherits all from Input.
- submit - submit the textarea (emits
submit). - cancel - cancel the textarea (emits
cancel). - readInput(callback) - grab key events and start reading text from the keyboard. takes a callback which receives the final value.
- readEditor(callback) - open text editor in
$EDITOR, read the output from the resulting file. takes a callback which receives the final value. - getValue() - the same as
this.value, for now. - clearValue() - clear input.
- setValue(text) - set value.
Textbox (from Textarea)
A box which allows text input.
Options:
- inherits all from Textarea.
- secret - completely hide text.
- censor - replace text with asterisks (
*).
Properties:
- inherits all from Textarea.
- secret - completely hide text.
- censor - replace text with asterisks (
*).
Events:
- inherits all from Textarea.
Methods:
- inherits all from Textarea.
Button (from Input)
A button which can be focused and allows key and mouse input.
Options:
- inherits all from Input.
Properties:
- inherits all from Input.
Events:
- inherits all from Input.
- press - received when the button is clicked/pressed.
Methods:
- inherits all from Input.
- press() - press button. emits
press.
ProgressBar (from Input)
A progress bar allowing various styles. This can also be used as a form input.
Options:
- inherits all from Input.
- orientation - can be
horizontalorvertical. - barFg, barBg - (completed) bar foreground and background.
(can be contained in
style: e.g.style.bar.fg). - ch - the character to fill the bar with (default is space).
- filled - the amount filled (0 - 100).
- value - same as
filled. - keys - enable key support.
- mouse - enable mouse support.
Properties:
- inherits all from Input.
Events:
- inherits all from Input.
- reset - bar was reset.
- complete - bar has completely filled.
Methods:
- inherits all from Input.
- progress(amount) - progress the bar by a fill amount.
- setProgress(amount) - set progress to specific amount.
- reset() - reset the bar.
FileManager (from List)
A very simple file manager for selecting files.
Options:
- inherits all from List.
- cwd - current working directory.
Properties:
- inherits all from List.
- cwd - current working directory.
Events:
- inherits all from List.
- cd - directory was selected and navigated to.
- file - file was selected.
Methods:
- inherits all from List.
- refresh([cwd], [callback]) - refresh the file list (perform a
readdironcwdand update the list items). - pick([cwd], callback) - pick a single file and return the path in the callback.
- reset([cwd], [callback]) - reset back to original cwd.
Checkbox (from Input)
A checkbox which can be used in a form element.
Options:
- inherits all from Input.
- checked - whether the element is checked or not.
- mouse - enable mouse support.
Properties:
- inherits all from Input.
- text - the text next to the checkbox (do not use setContent, use
check.text = ''). - checked - whether the element is checked or not.
- value - same as
checked.
Events:
- inherits all from Input.
- check - received when element is checked.
- uncheck received when element is unchecked.
Methods:
- inherits all from Input.
- check() - check the element.
- uncheck() - uncheck the element.
- toggle() - toggle checked state.
RadioSet (from Box)
An element wrapping RadioButtons. RadioButtons within this element will be mutually exclusive with each other.
Options:
- inherits all from Box.
Properties:
- inherits all from Box.
Events:
- inherits all from Box.
Methods:
- inherits all from Box.
RadioButton (from Checkbox)
A radio button which can be used in a form element.
Options:
- inherits all from Checkbox.
Properties:
- inherits all from Checkbox.
Events:
- inherits all from Checkbox.
Methods:
- inherits all from Checkbox.
Terminal (from Box)
A box which spins up a pseudo terminal and renders the output. (Requires term.js to be installed).
Options:
- inherits all from Box.
Properties:
- inherits all from Box.
Events:
- inherits all from Box.
Methods:
- inherits all from Box.
Image (from Box)
Display an image in the terminal (jpeg, png, gif) using w3mimgdisplay. Requires w3m to be installed. X11 required: works in xterm, urxvt, and possibly other terminals.
Options:
- inherits all from Box.
- file - path to image
- w3m - path to w3mimgdisplay
Properties:
- inherits all from Box.
Events:
- inherits all from Box.
Methods:
- inherits all from Box.
- setImage(img, callback) - set the image in the box to a new path.
- clearImage(callback) - clear the current image.
- imageSize(img, callback) - get the size of an image file in pixels.
- termSize(callback) - get the size of the terminal in pixels.
Positioning
Offsets may be a number, a percentage (e.g. 50%), or a keyword (e.g.
center).
Dimensions may be a number, or a percentage (e.g. 50%).
Positions are treated almost exactly the same as they are in CSS/CSSOM when
an element has the position: absolute CSS property.
When an element is created, it can be given coordinates in its constructor:
var box = blessed.box({
left: 'center',
top: 'center',
bg: 'yellow',
width: '50%',
height: '50%'
});
This tells blessed to create a box, perfectly centered relative to its parent, 50% as wide and 50% as tall as its parent.
To access the calculated offsets, relative to the parent:
console.log(box.rleft);
console.log(box.rtop);
To access the calculated offsets, absolute (relative to the screen):
console.log(box.left);
console.log(box.top);
Overlapping offsets and dimensions greater than parents'
This still needs to be tested a bit, but it should work.
Content
Every element can have text content via setContent. If tags: true was
passed to the element's constructor, the content can contain tags. For example:
box.setContent('hello {red-fg}{green-bg}{bold}world{/bold}{/green-bg}{/red-fg}');
To make this more concise {/} cancels all character attributes.
box.setContent('hello {red-fg}{green-bg}{bold}world{/}');
Newlines and alignment are also possible in content.
box.setContent('hello\n'
+ '{right}world{/right}\n'
+ '{center}foo{/center}');
This will produce a box that looks like:
| hello |
| world |
| foo |
Content can also handle SGR escape codes. This means if you got output from a
program, say git log for example, you can feed it directly to an element's
content and the colors will be parsed appropriately.
This means that while {red-fg}foo{/red-fg} produces ^[[31mfoo^[[39m, you
could just feed ^[[31mfoo^[[39m directly to the content.
Event Bubbling
Events can bubble in blessed. For example:
Receiving all click events for box:
box.on('click', function(mouse) {
box.setContent('You clicked ' + mouse.x + ', ' + mouse.y + '.');
screen.render();
});
Receiving all click events for box, as well as all of its children:
box.on('element click', function(el, mouse) {
box.setContent('You clicked '
+ el.type + ' at ' + mouse.x + ', ' + mouse.y + '.');
screen.render();
if (el === box) {
return false; // Cancel propagation.
}
});
el gets passed in as the first argument. It refers to the target element the
event occurred on. Returning false will cancel propagation up the tree.
Rendering
To actually render the screen buffer, you must call render.
box.setContent('Hello world.');
screen.render();
Elements are rendered with the lower elements in the children array being painted first. In terms of the painter's algorithm, the lowest indicies in the array are the furthest away, just like in the DOM.
Testing
- For an interactive test, see
test/widget.js. - For a less interactive position testing, see
test/widget-pos.js.
Lower-Level Usage
This will actually parse the xterm terminfo and compile every string capability to a javascript function:
var blessed = require('blessed')
, tput = blessed.tput('xterm-256color');
console.log(tput.setaf(4) + 'hello' + tput.sgr0());
To play around with it on the command line, it works just like tput:
$ tput.js setaf 2
$ tput.js sgr0
$ echo "$(tput.js setaf 2)hello world$(tput.js sgr0)"
The main functionality is exposed in the main blessed module:
var blessed = require('blessed')
, program = blessed.program();
program.key('q', function(ch, key) {
program.clear();
program.disableMouse();
program.showCursor();
program.normalBuffer();
process.exit(0);
});
program.on('mouse', function(data) {
if (data.action === 'mousemove') {
program.move(data.x, data.y);
program.bg('red');
program.write('x');
program.bg('!red');
}
});
program.alternateBuffer();
program.enableMouse();
program.hideCursor();
program.clear();
program.move(1, 1);
program.bg('black');
program.write('Hello world', 'blue fg');
program.setx((program.cols / 2 | 0) - 4);
program.down(5);
program.write('Hi again!');
program.bg('!black');
program.feed();
FAQ
- Why doesn't the Linux console render lines correctly on Ubuntu?
You need to install the
ncurses-basepackage and thencurses-termpackage. (#98) - Why do vertical lines look chopped up in iTerm2? All ACS vertical lines look this way in iTerm2.
- Why can't I use my mouse in Terminal.app? Terminal.app does not support mouse events.
- Why doesn't the Image element appear in my terminal? The Image element uses w3m to display images. This generally only works on X11+xterm/urxvt, but it may work on other unix terminals.
- Why can't my mouse clicks register beyond 255-287 cells? Older versions of VTE do not support any modern mouse protocol. On top of that, the old x10 protocol it does implement is bugged. Through several workarounds we've managed to get the cell limit from 127 to 255/287. If you're not happy with this, you may want to look into using xterm or urxvt, or a terminal which uses a modern VTE, like gnome-terminal.
- Is blessed efficient? Yes. Blessed implements CSR and uses the painter's algorithm to render the screen. It maintains two screen buffers so it only needs to render what has changed on the terminal screen.
- Will blessed work with all terminals? Yes. blessed has a terminfo/termcap parser and compiler that was written from scratch. It should work with every terminal as long as a terminfo file is provided. If you notice any compatibility issues in your termial, do not hesitate to post an issue.
Contribution and License Agreement
If you contribute code to this project, you are implicitly allowing your code
to be distributed under the MIT license. You are also implicitly verifying that
all code is your original work. </legalese>
License
Copyright (c) 2013, Christopher Jeffrey. (MIT License)
See LICENSE for more info.